What is an EMF
An electromotive force is a force that pushes electrons in one direction. Why it is so important? If you read the article about electric current, then probably remember the main condition of the appearance of electric current: one direction. Yes, this direction can change over time, but the principle remains the same. The electrons in the conductor must move synchronously in any direction.
But how can this be achieved? After all, free electrons in a conductor are always in a chaotic state.
So, in order for electrons to run in the same direction, you need some kind of force to do it.
Hydraulic analogy
So let’s get back to the article on electric current. Imagine a garden hose with water in it.
Therefore, the water does not run from it.

But once the water molecules are running in one direction, the garden hose will have the pressure of the water, and it will come out of the garden hose.
So the water will flow out of it.
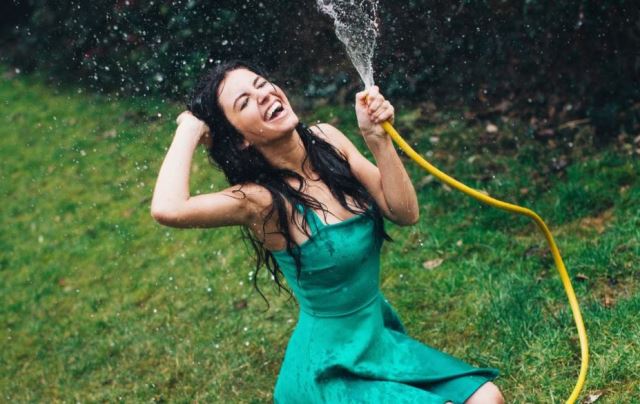

Can you see the difference?
But who or what pushes the water in the hose? Have you ever thought about it? The answer is a water pump. He might look something like this:
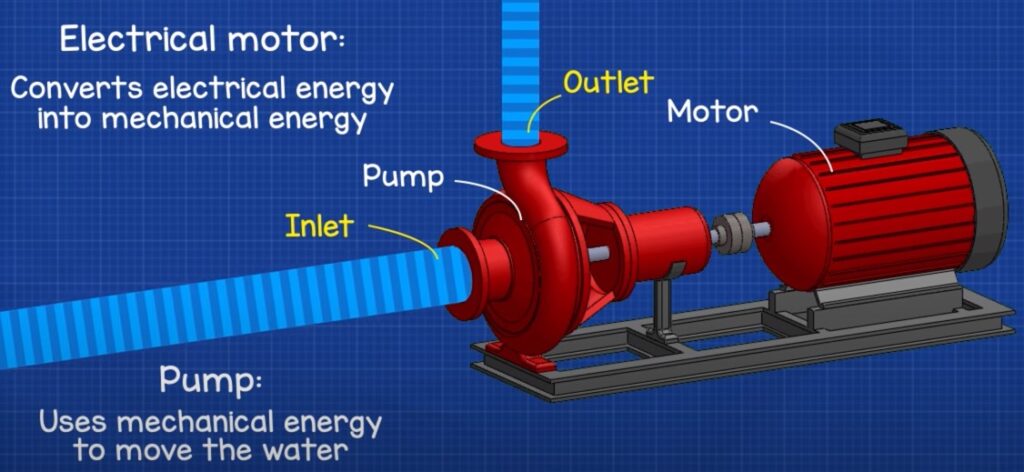
In this case, the water pump fills the water tower.
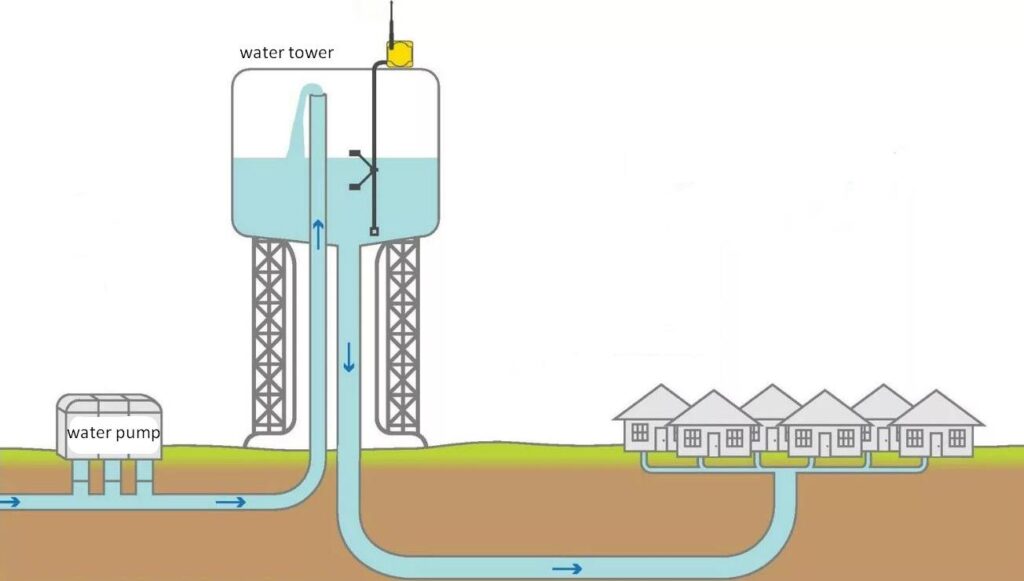
So now we know that the water pressure in the hose can be created by a water pump.
Emf generators
So, what do we need to push electrons in the same direction? We need an EMF generator. They are also called electric current sources. There are several basic ways to get EMF. Let’s look some of them.
The electromotive force, like voltage, is measured in volts.
Electrochemical current sources
This includes batteries of all types. We use them everywhere in our lives. They all give a direct current.



Photovoltaic Current Sources
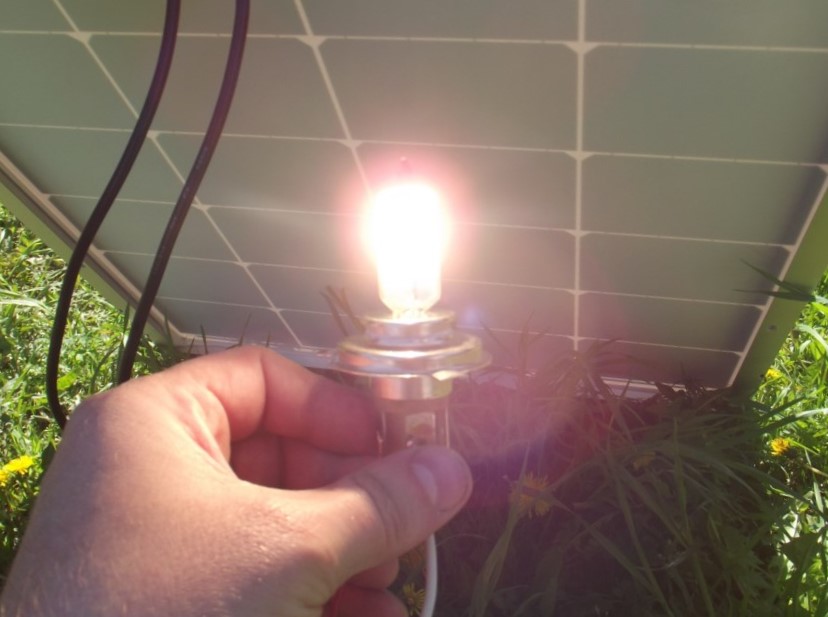
In this case, solar panels are used to generate electric current.
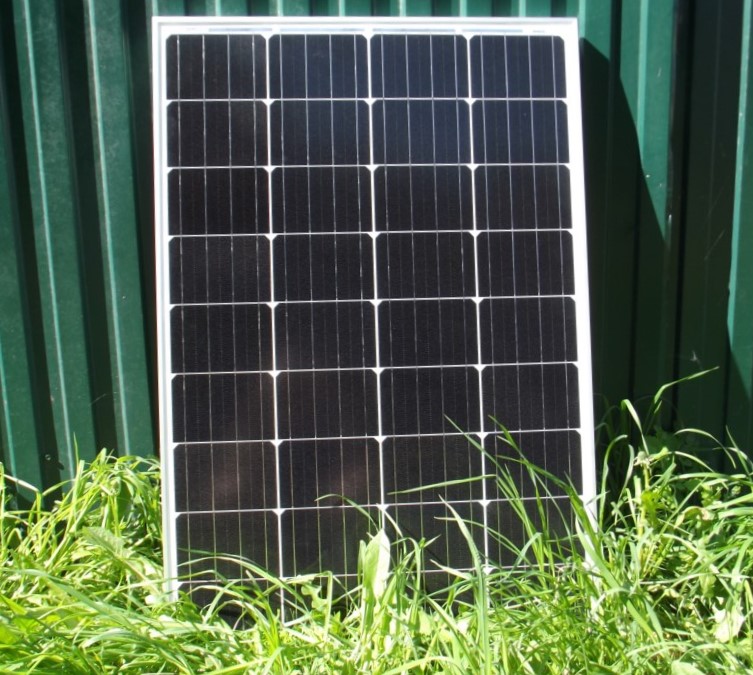

As you can see, this panel lights up the halogen lamp without a problem.

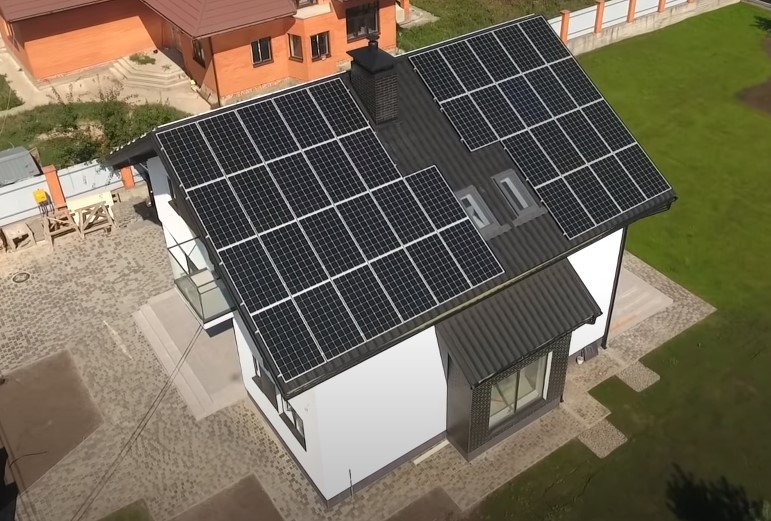
In some houses, you can see these solar panels on the roof.

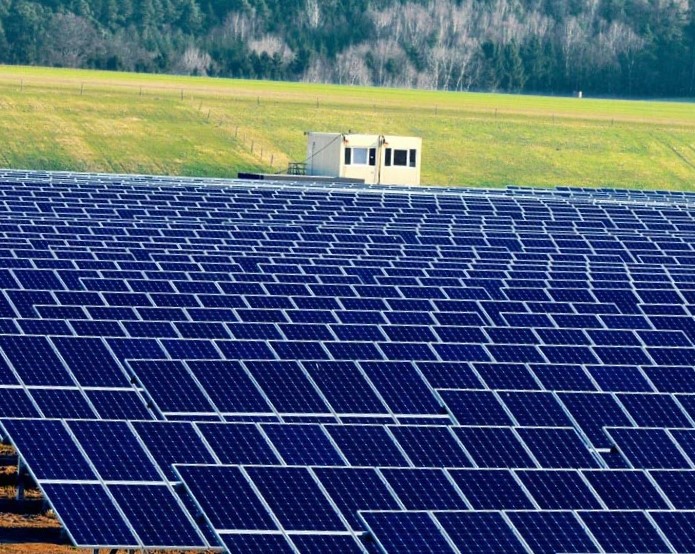
In countries with a lot of sunlight, they build whole plantations of solar panels.

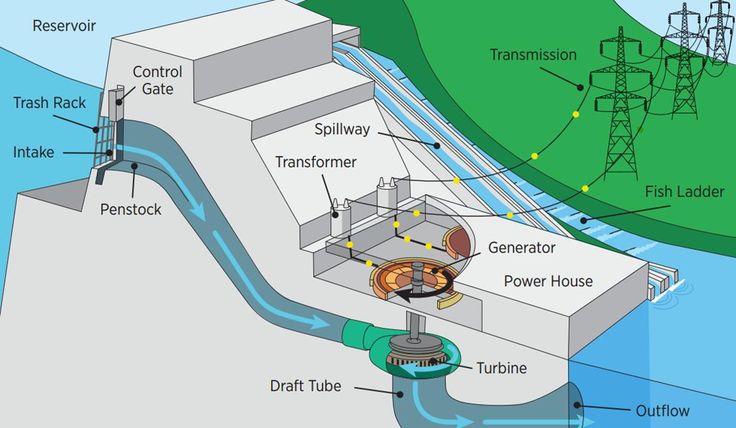
Induction generators
Currently, these are the most common sources of electrical current. It uses the principle of electromagnetic induction. The electrical current in your home outlets comes from a generator based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. The generator is a large motor, the shaft of which is rotated by some kind of force. This can be the force of falling water or the force of steam.
Thermo EMF
The Seebeck effect is the electromotive force (emf) that develops across two points of an electrically conducting material when there is a temperature difference between them. The emf is called the Seebeck emf (or thermo/thermal/thermoelectric emf).
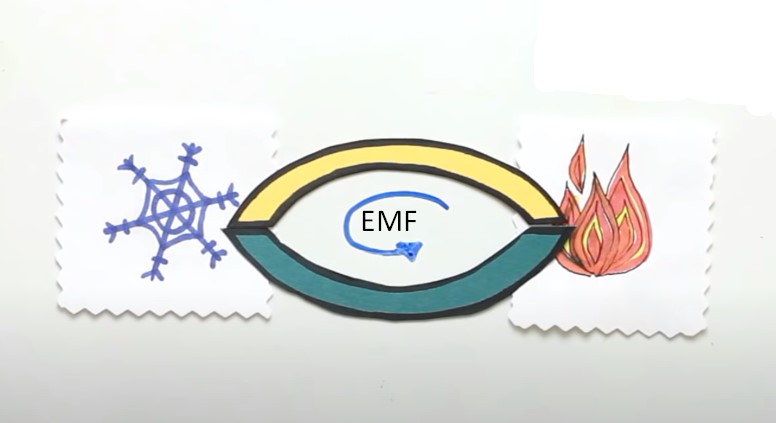
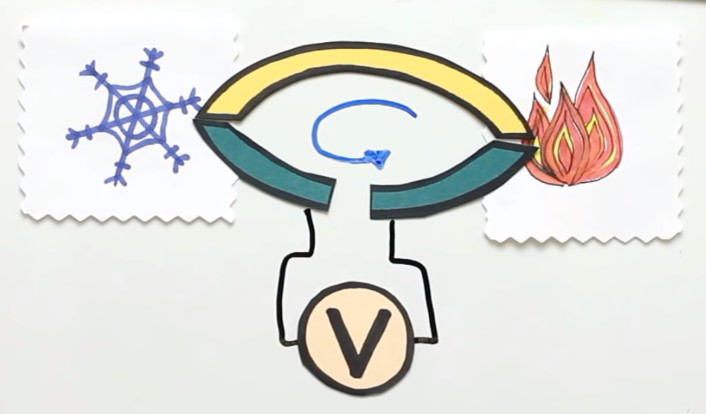
Let’s understand this effect in more detail. A closed circuit of two different metals is called a thermocouple.
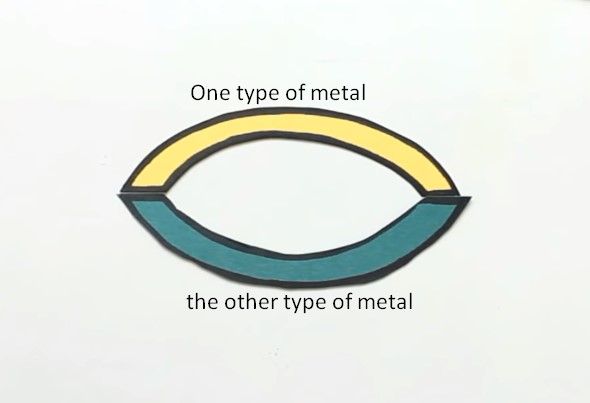
If you keep the joints of the plates at different temperatures, then in this closed circuit will create an EMF.

In order to measure it, let’s cut one of the plates and connect a voltmeter there. You can see the EMF value on the voltmeter.
Conclusion
The electromotive force is the force that generates an electric current and keeps it going for a long time. The main task of EMF is to push electrons in any one direction for a long period of time. To put it simply in one sentence, the electromotive force is a pump for electrons, and the types of pumps can be completely different.








